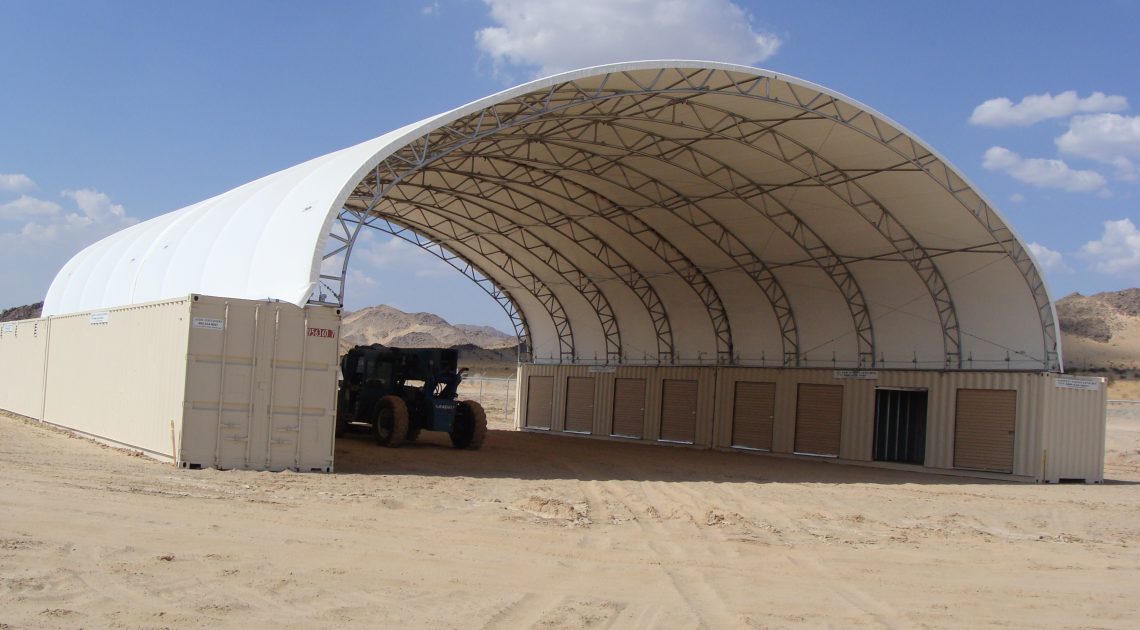
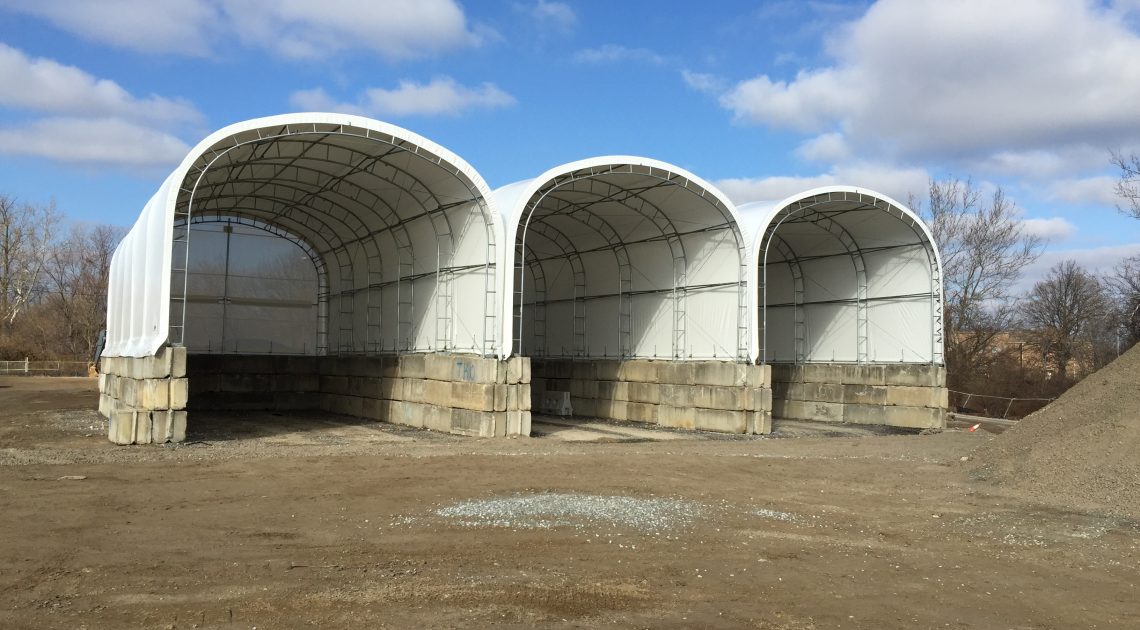
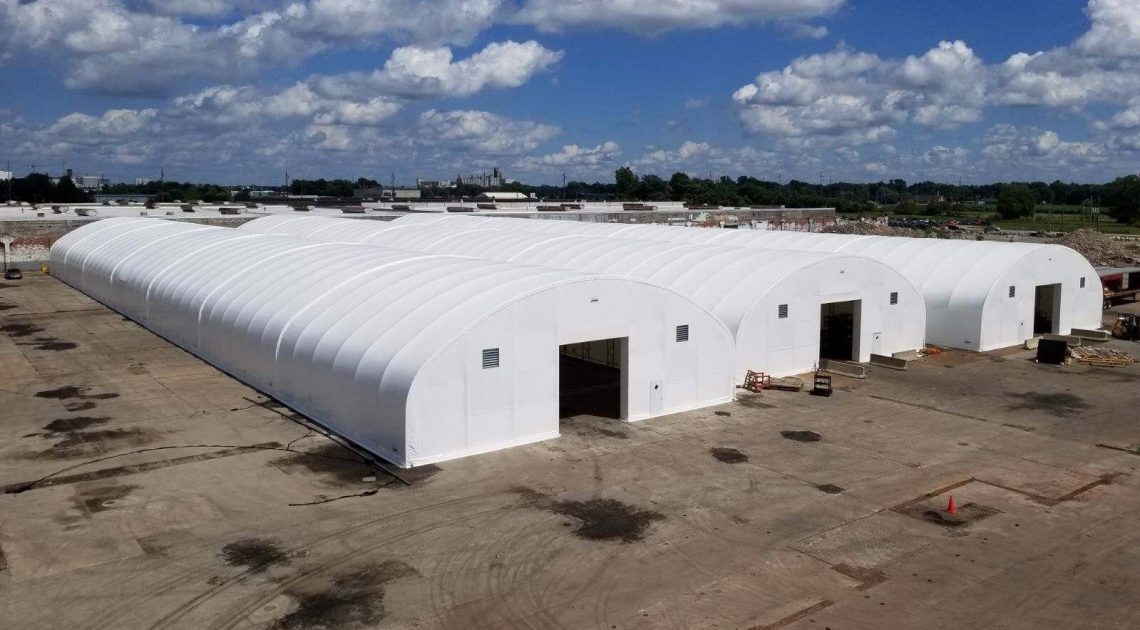
When manufacturing tarps, choosing the right material is crucial. PVC and polyethylene are two of the most common tarp materials, but which is the better option? Leave it up to the experts to help you compare PVC and polyethylene and see which comes out on top.
PVC and Its Key Characteristics
PVC is a synthetic thermoplastic material that comes from ethylene and chlorine. It has impressive strength, durability, and resistance to various chemical and environmental factors. Some of the key characteristics of PVC include:
- High tensile strength: PVC boasts impressive tensile strength, making it a sturdy and reliable material for various applications.
- Weather resistance: PVC exhibits excellent resistance to weathering, including exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, water, and extreme temperatures.
- Chemical resistance: PVC is highly resistant to acids, bases, and salts, making it an ideal material for various industrial and chemical applications.
- Low cost: PVC is generally less expensive than other plastic materials, so it’s an enticing option for large-scale projects or budget-conscious buyers.
Polyethylene and Its Key Characteristics
Polyethylene is a member of the polyolefin family and comes from ethylene through a polymerization process. It’s lightweight, flexible, and corrosion resistant, making it ideal for various applications. Key characteristics of polyethylene include:
- Flexibility: Polyethylene is highly flexible, allowing it to easily conform to various shapes and designs without cracking or breaking.
- Impact resistance: Polyethylene offers excellent impact resistance, so it’s a durable option for applications that require materials to resist impact or sudden forces.
- Chemical resistance: Like PVC, polyethylene is highly resistant to most chemicals, making it suitable for industrial and chemical applications.
Comparing PVC and Polyethylene
Now that we know more about PVC and polyethylene, the real question is, “Which one comes out on top?” To answer that question, let’s look at the pros and cons of each.
Advantages of PVC
PVC stands out primarily due to its high tensile strength, making it an excellent choice for heavy-duty applications. Its superb weather resistance renders it suitable for outdoor applications, as it can withstand harsh environmental conditions without significant degradation.
Disadvantages of PVC
Although engineers are working on creating more sustainable forms of PVC, there’s still lots of room for improvement in this respect. The PVC production process releases harmful toxins and isn’t typically recyclable, leading to a large amount of plastic waste. Furthermore, PVC’s resistance to UV radiation is imperfect. As a result, it’ll degrade with prolonged exposure to sunlight.
Advantages of Polyethylene
This material’s superior impact resistance also makes it an ideal choice for applications requiring resilience against sudden physical forces. Like PVC, polyethylene possesses commendable chemical resistance, making it suitable for use in industrial and chemical arenas where exposure to harsh chemicals is common.
Disadvantages of Polyethylene
Polyethylene lacks the high tensile strength that PVC boasts, which can limit its use in applications where high structural strength is necessary. Furthermore, weather-resistant polyethylene is less resistant to UV radiation than PVC and, therefore, can degrade over time when exposed to prolonged sunlight.
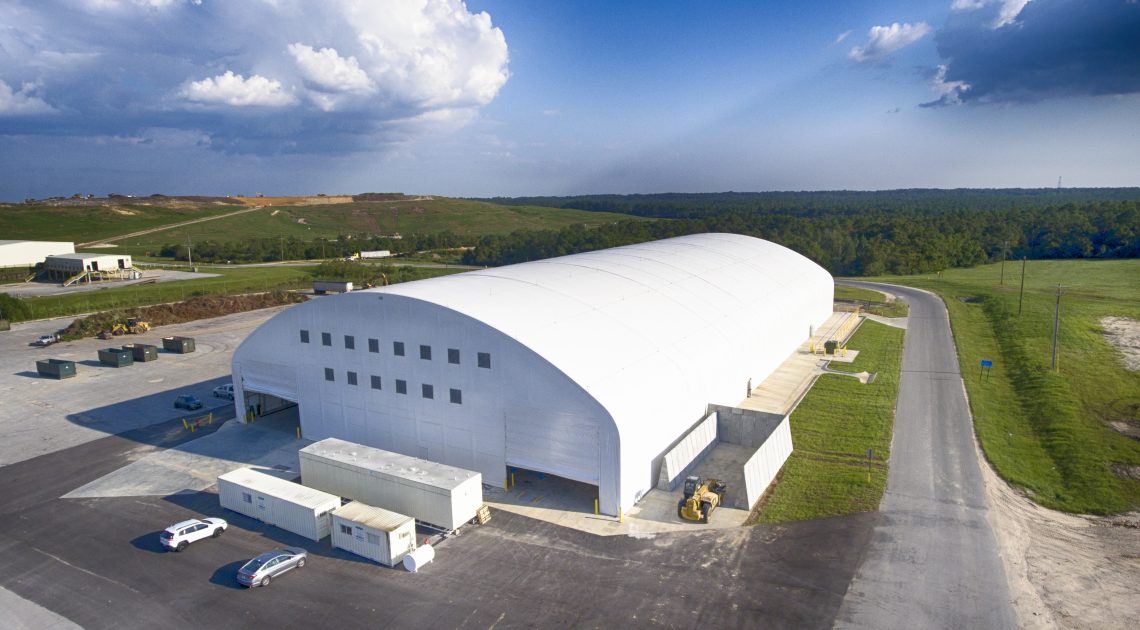
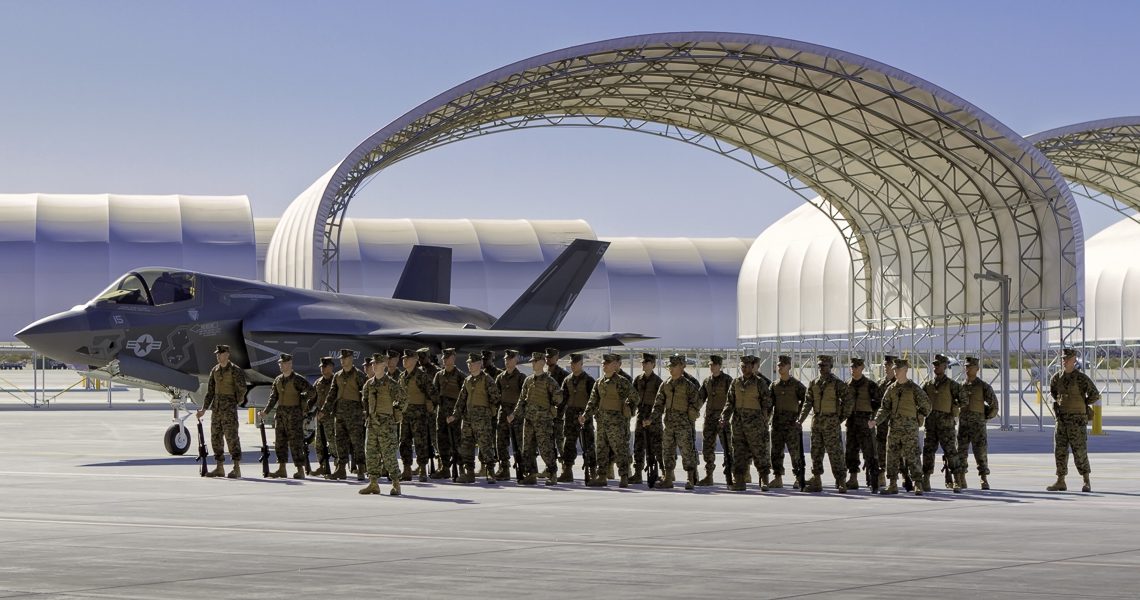
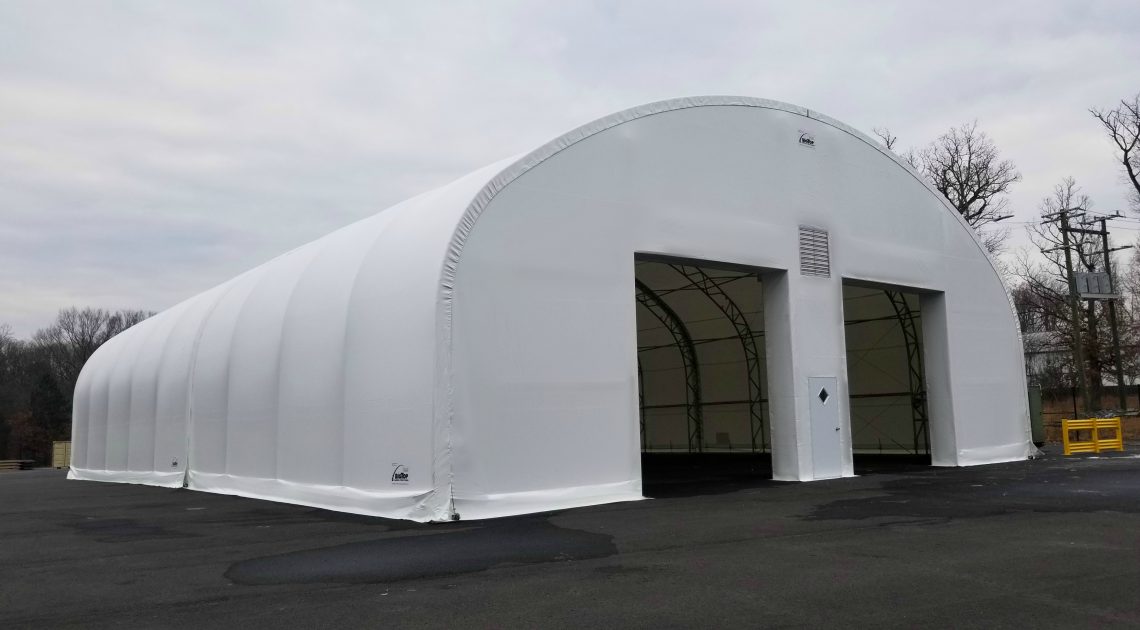
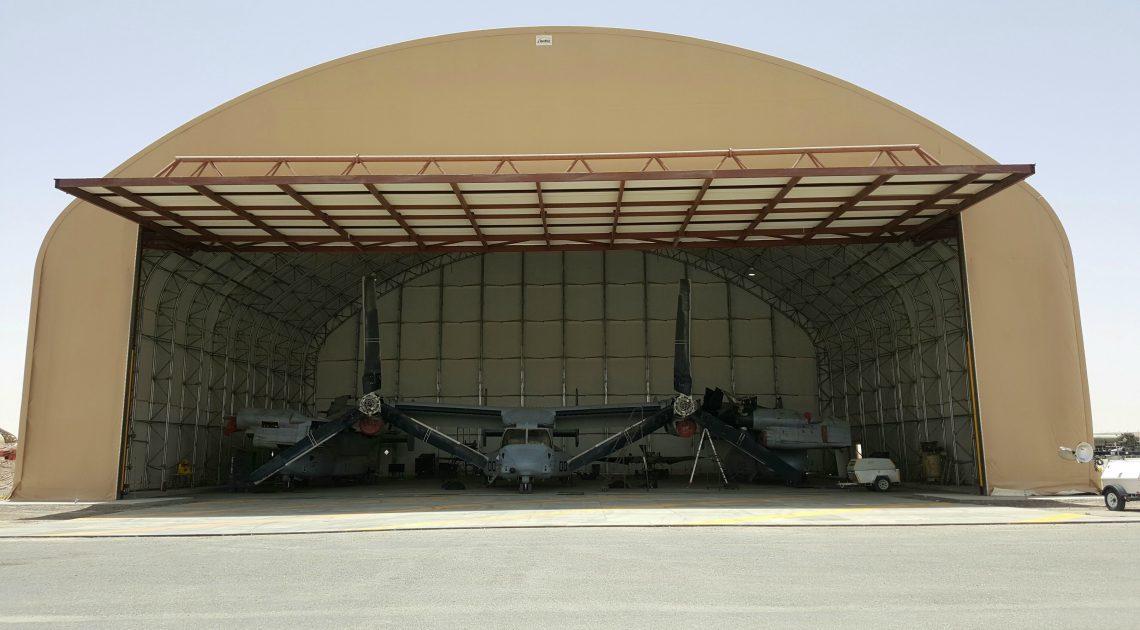
For heavy-duty, rugged applications, PVC is often the best and most affordable option. That’s why, at Big Top Manufacturing, we make all our large fabric structures with PVC tarps so that you can rely on your structure regardless of the conditions.
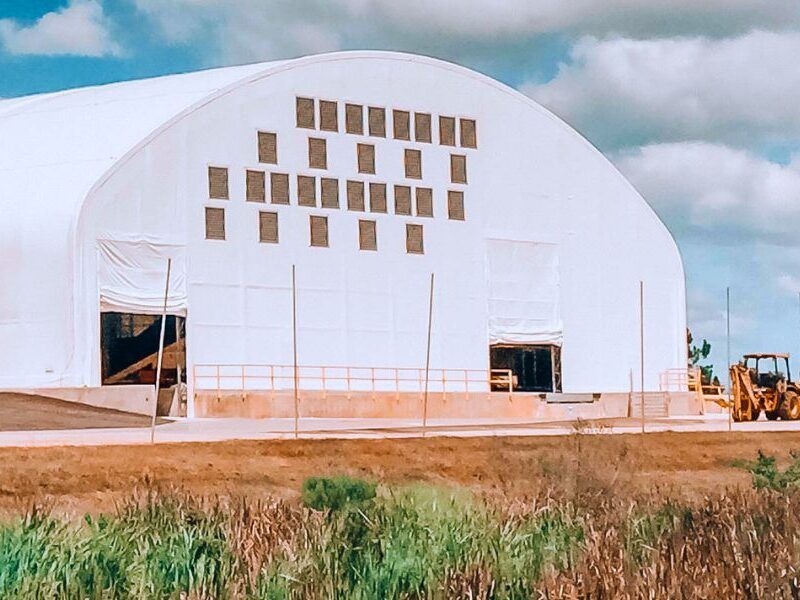

























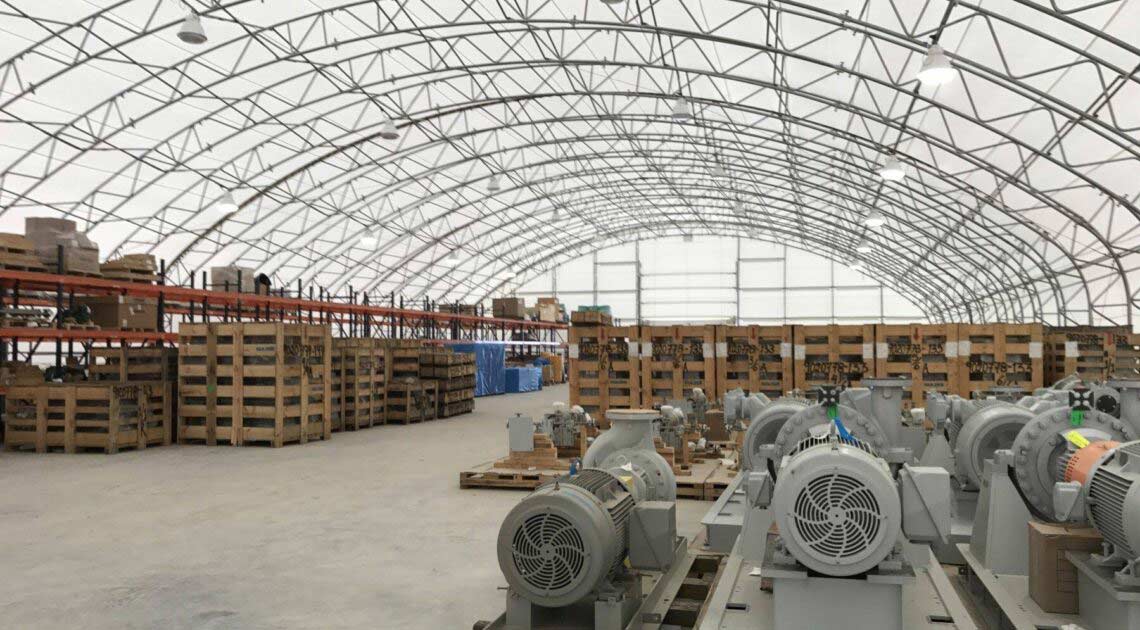
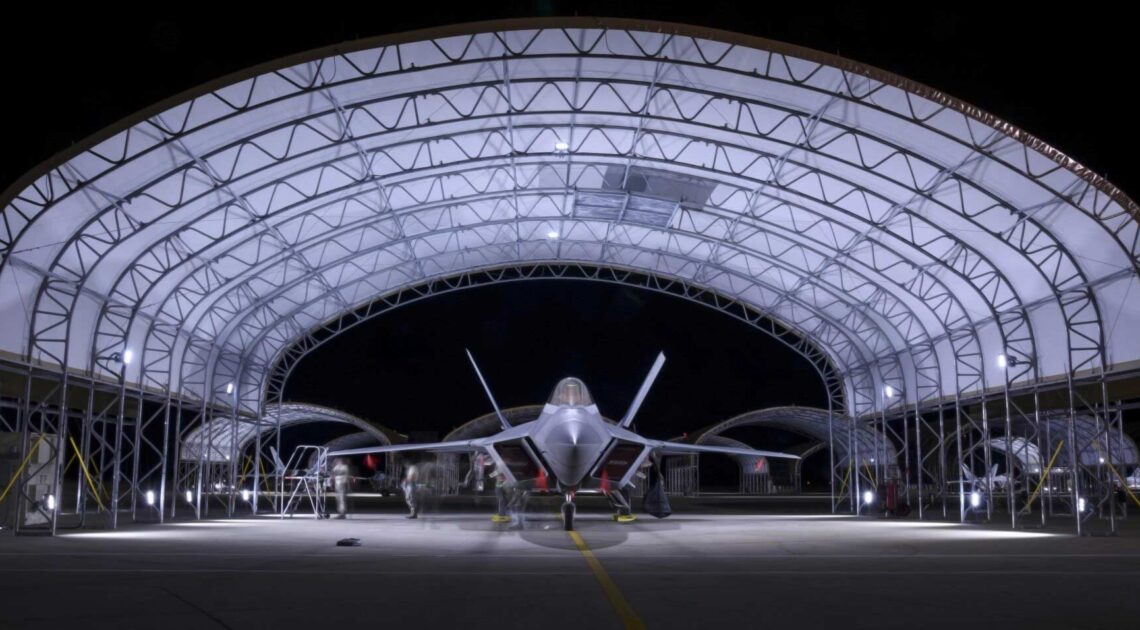
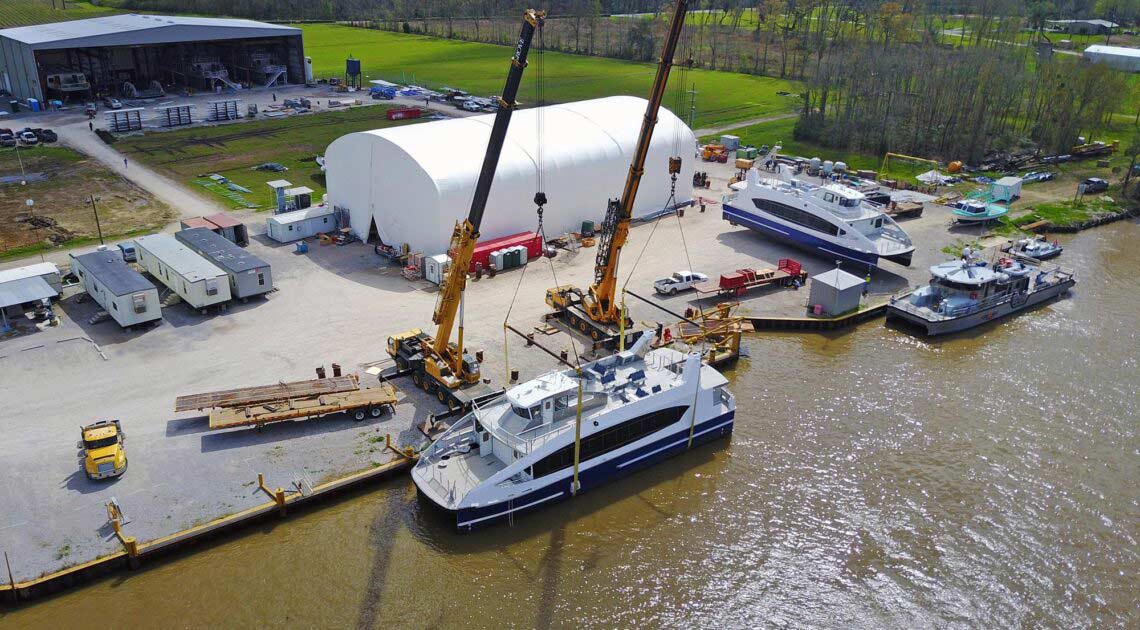
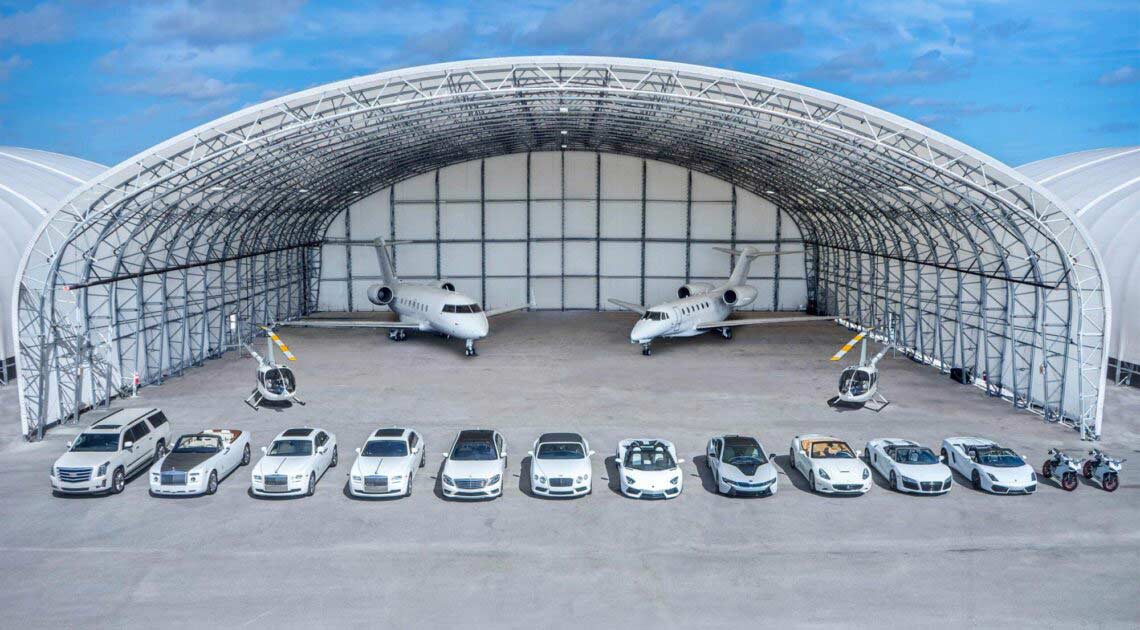
 The ideal solution is to have a structure that can protect valuable assets and employees from the elements. In many cases, the need for this type of structure is specific to any given business, which means that the building needs to be adaptable so it can meet a specific set of requirements. At Big Top Fabric Structures, this is our specialty; as a custom manufacturer, we make buildings that are designed to accommodate many different specific needs. Our fabric buildings have been used for a variety of applications by businesses within the construction industry and beyond.
The ideal solution is to have a structure that can protect valuable assets and employees from the elements. In many cases, the need for this type of structure is specific to any given business, which means that the building needs to be adaptable so it can meet a specific set of requirements. At Big Top Fabric Structures, this is our specialty; as a custom manufacturer, we make buildings that are designed to accommodate many different specific needs. Our fabric buildings have been used for a variety of applications by businesses within the construction industry and beyond.




































